1. Brief Introduction
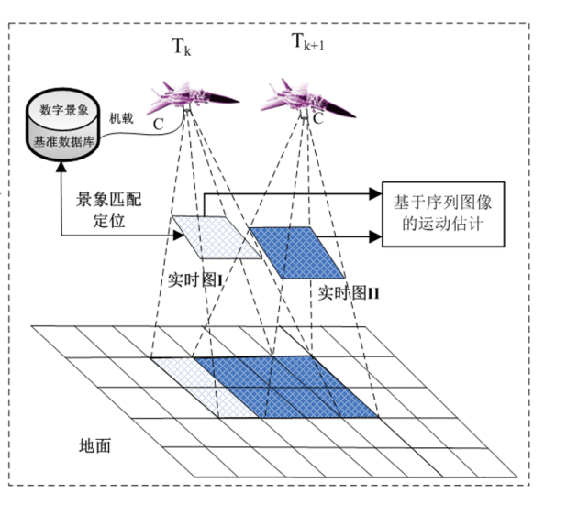
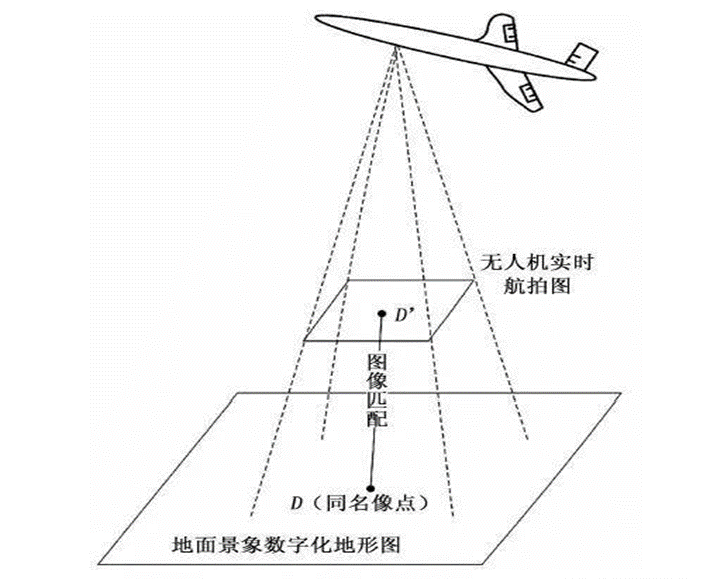
In areas where satellite navigation is unavailable, drones will lose their way. The Visual Navigation System (VNS) for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) continuously captures ground imagery along the flight path using an onboard downward-facing camera. By comparing this imagery with pre-stored satellite remote sensing data, the system determines the UAV’s current position and orientation. This enables real-time correction of position, attitude, and velocity errors in the onboard inertial navigation system, providing high-precision navigation information for UAVs operating in satellite-denied environments.
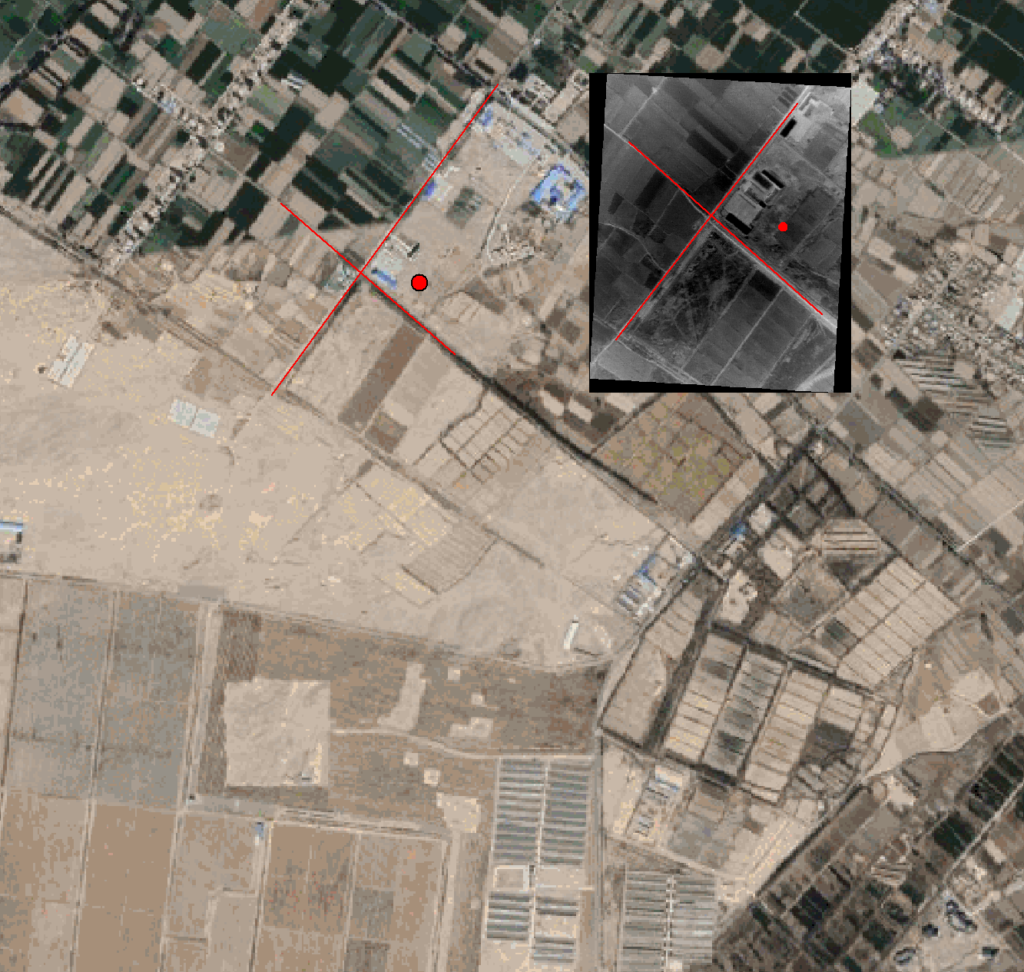
Schematic Diagram of Drone Visual Positioning

2. Product System
a. KT-200 Main Parameters
Navigation accuracy: Positioning accuracy 10m~80m (corresponding flight altitude: 200m to 12,000m)
Processing time: Continuous output frequency 0.25Hz~1Hz (depending on the accuracy of the inertial navigation system)
Working Conditions: Relative altitude: 500m–12,000m, Speed: 0~200m/s, Attitude: heading: -180°~180° roll: -25°~25° Pitch: -15°~15°
Continuous navigation time: No limit
Applicable Environment: No rain, fog, snow, dust storms, etc., which can affect infrared imaging
Weight: 220g
System Basic Requirements: The infrared camera features self-calibration, unconstrained flight paths, and an onboard reference map.
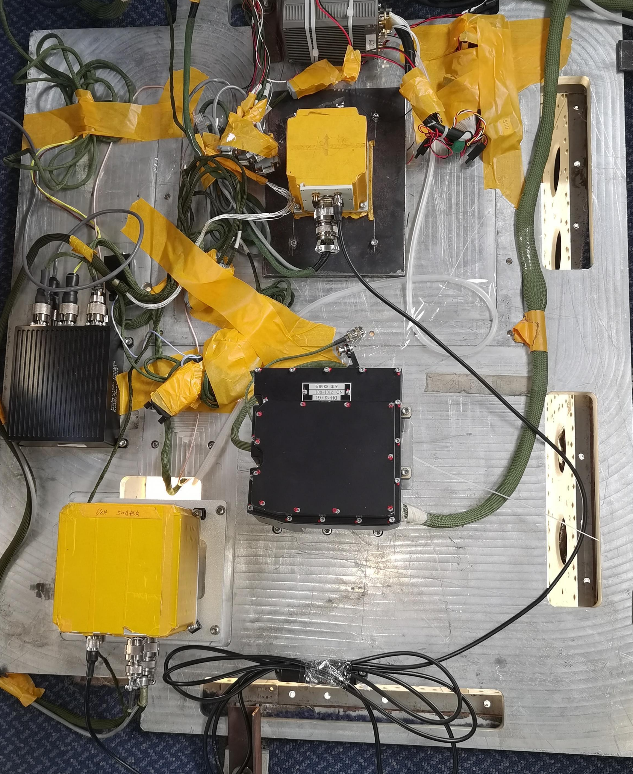
b. System Composition
The system consists of a visual navigation device, visual navigation software, connecting cables, and other components. The visual navigation system can be directly connected to the inertial navigation system or relay relevant navigation information through the flight controller.
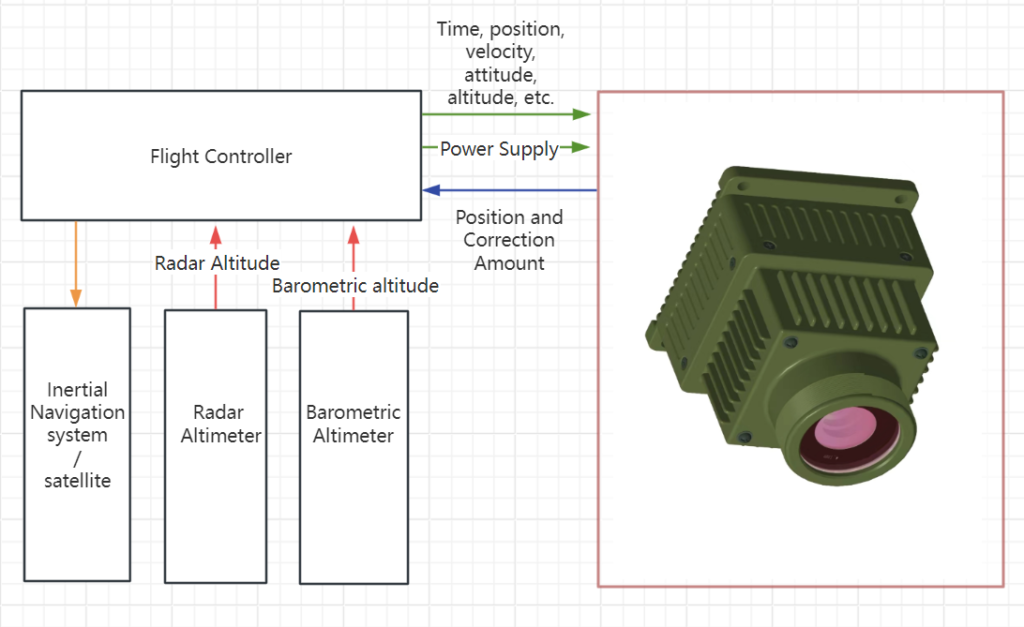
C. System Schematic Diagram

d. Uncooled Infrared Imaging Module

Resolution: 640 x 512
Pixel Size: 12μm
Infrared Band: 8~12μm
Field of View: 90°
Image Output Frame Rate: 50Hz
e. Information Processing Circuit
Includes: RK3588, power supply circuit unit, video input interface unit, DDR memory unit, eMMC storage unit, serial communication RS422, Ethernet communication, USB communication, and other interfaces.
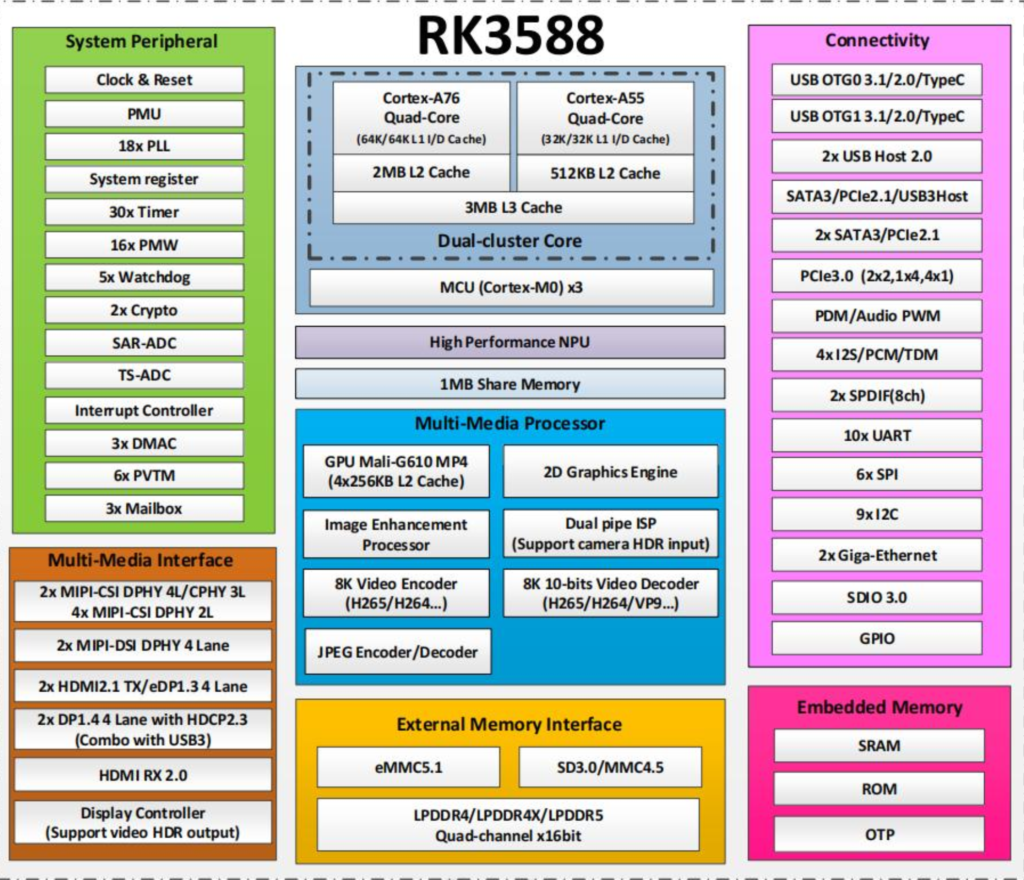
f. Visual Navigation Software
Features system self-test, system communication, matching processing, reference image data maintenance, and software upgrades. The software was developed, compiled, and linked under the Ubuntu environment.
g. Aircraft Installation Requirements
The relative accuracy between the camera mounting surface and the inertial navigation mounting reference surface must be appropriately controlled, with an unobstructed field of view.
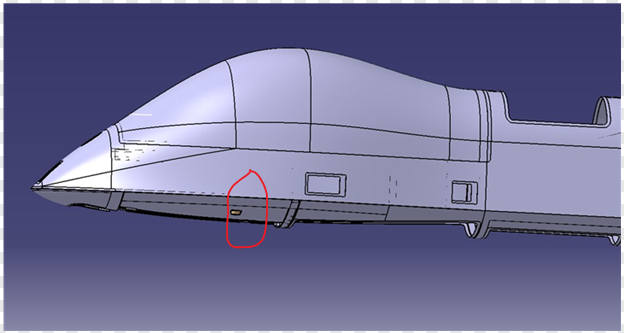
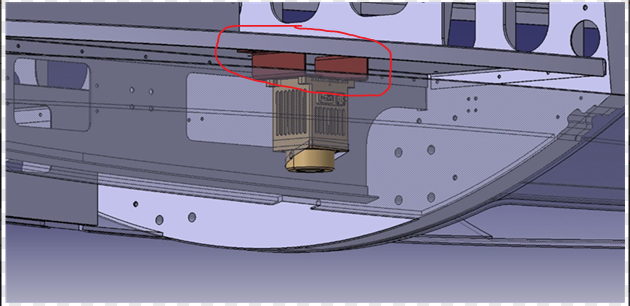
h. Ground-Based System
Comprising a portable ruggedized computer and benchmark data creation and binding software, it provides benchmark map updates and system maintenance functions.
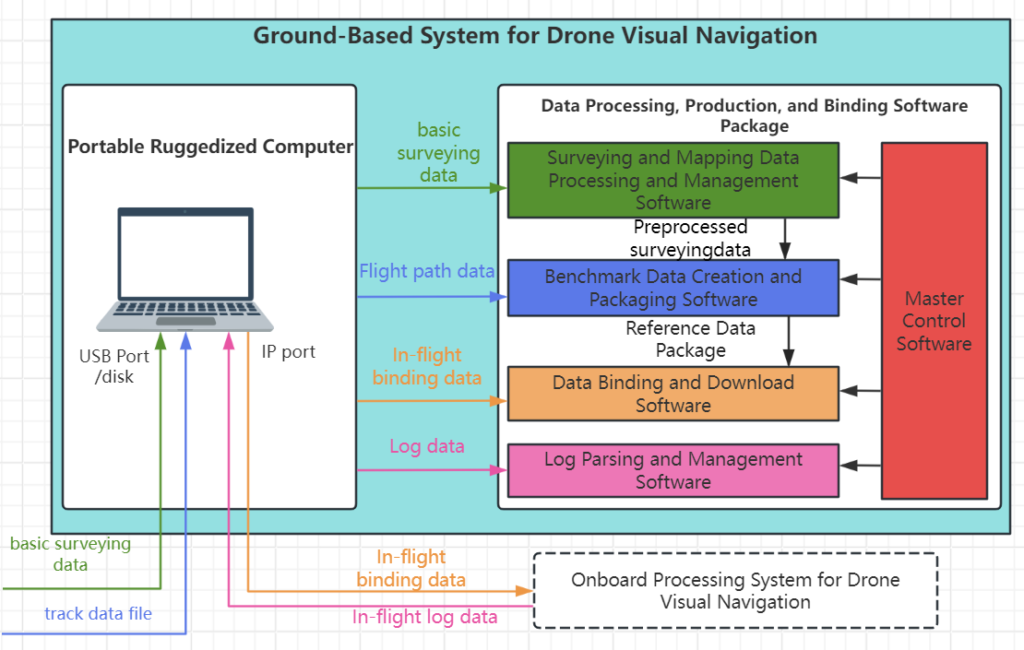
The system can preload base maps covering an area of no less than 5 million square kilometers. The users don’t need to provide base maps. (orthophotoquad, DOM, 10-meter resolution) (topographic map, DEM, 25-meter resolution)
i: Important Notes
- Pre-mission preparations: confirm whether the flight mission area extends beyond the pre-uploaded reference map area. Ground systems can be used to generate and load reference maps as needed.
- Before the aircraft takes off: Remove the lens cap from the camera. The system powers up and performs a self-test. Upon completion, it transmits the self-test results to the higher-level system.
- During the mission, the visual navigation system operates automatically based on aircraft status, periodically sending navigation results to the flight controller; it automatically generates log files to record relevant information.
- After the aircraft lands, the visual navigation system automatically ceases operation based on the aircraft’s status. Log files can be downloaded using the ground system. And please remember to attach the lens cap to the camera.
j: Main Features
- Fully Autonomous Navigation, The visual navigation module continuously corrects inertial navigation position and velocity errors throughout the flight, enabling the drone to maintain high-precision navigation at all times.
- Adaptability for any time of day, any terrain, adaptable to daytime, nighttime, mountainous, urban, suburban, farmland, and desert terrain conditions.
- Low maintenance, hassle-free, and easy to use, the system features self-calibration, incorporates a wide-range reference map, requires no flight route planning or flight constraints, and operates fully automatically throughout the entire process.
- Low-cost, high-precision, full-parameter navigation, utilizing low-cost uncooled infrared cameras and a universal information processing system, combined with inertial navigation to achieve high-precision full-parameter navigation.
3. Product Tests
a. From June 11 to 12, 2023, environmental tests were conducted on the visual navigation system at the experimental center. The test items included low-temperature operation, low-temperature storage, high-temperature operation, high-temperature storage, random vibration, and impact tests. The test results before, during, and after each test were normal, and the test results met the requirements.




b. From June to December 2023, we completed wet heat testing, power supply characteristic testing, and electromagnetic compatibility testing, and conducted salt spray testing analysis on typical materials.
| Test phase | Temperature | Relative humidity | Time | No. Of Cycles | Test tolerance |
| Warming up | 30~60℃ | 95% | 2h | 10 | Temperature: ±2℃ Relative Humidity: ±5% |
| High temperature and high humidity | 60℃ | 95% | 6h | 10 | Temperature: ±2℃ Relative Humidity: ±5% |
| Cooling down | 60~30℃ | >85% | 8h | 10 | Temperature: ±2℃ Relative Humidity: ±5% |
| Room temperature and high humidity | 30℃ | 95% | 8h | 10 | Temperature: ±2℃ Relative Humidity: ±5% |
c. Electromagnetic compatibility project limit value curve

The system has undergone 4 years of flight testing, and its main performance meets the specified requirements.
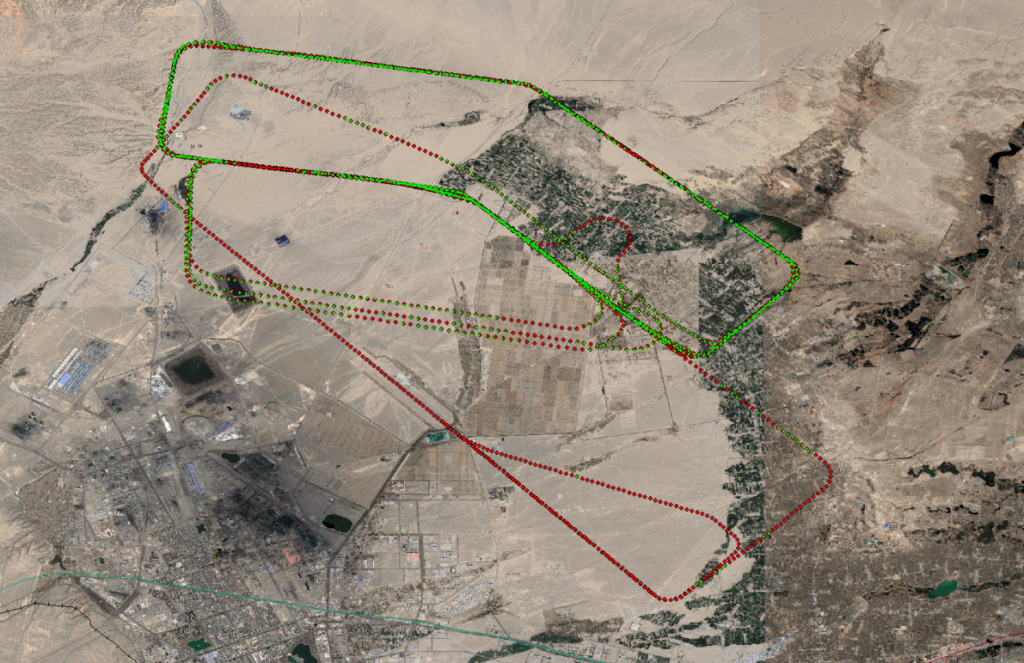
d. (2022 Jiayuguan Test Results) In 2022, real-time positioning tests were conducted, with a total of three flights lasting 13 hours. The flight altitude ranged from 500 meters to 6,500 meters, and the flight area covered various terrains and landforms near Jiayuguan, including suburban areas, deserts, farmlands, and mountainous areas.

(First flight test results) A total of 2,235 real-time positioning matches were made, of which 2,195 were valid positioning data with an altitude greater than 450 meters. (The red dots represent the GPS-located flight path, and the green dots represent the available positioning results output.)
(Second flight test results)A total of 3,116 real-time results were obtained, and 2,161 data points were deemed usable for the flight controller.
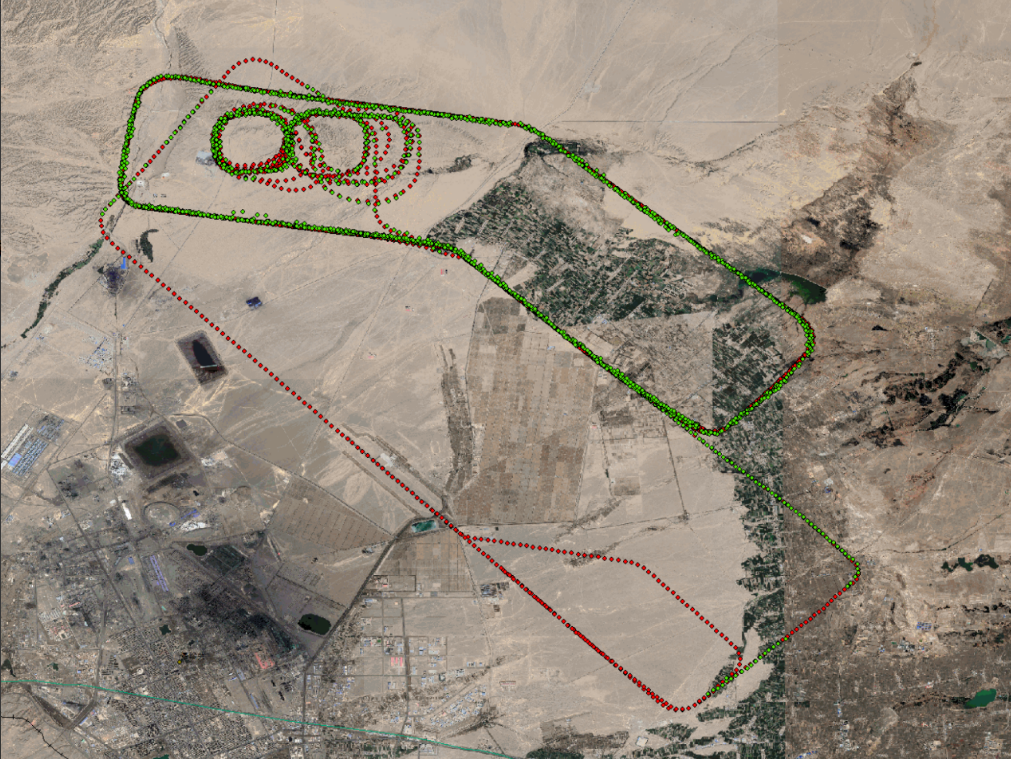
(Summary of all results) During the test, a total of 9,681 navigation results were sent to the drone’s flight controller. Among these, 6,417 results marked as usable by the flight controller were included in the data frames; two of the results were inaccurate. The accuracy rate of the results is 99.96%.
| Flight altitude (m) | latitude | longitude | Latitude correction accuracy | Longitude correction accuracy | North speed correction accuracy | East speed correction accuracy |
| Below 500m | 11.15 | 8.06 | 8.07 | 9.01 | 0.090 | 0.096 |
| 500~1500 | 16.24 | 13.69 | 8.07 | 9.01 | 0.090 | 0.096 |
| 1500~2500 | 21.62 | 19.10 | 13.84 | 11.73 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| 2500~3500 | 28.63 | 27.16 | 25.07 | 24.54 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| 3500~4500 | 41.50 | 40.39 | 37.69 | 35.28 | 0.33 | 0.36 |
| 4500~5500 | 54.50 | 47.93 | 48.76 | 48.33 | 0.32 | 0.37 |
| 5500~6500 | 81.77 | 81.26 | 48.76 | 48.33 | 0.32 | 0.37 |
| Comprehensive statistics | 37.91 | 35.55 | 30.81 | 30.03 | 0.22 | 0.25 |
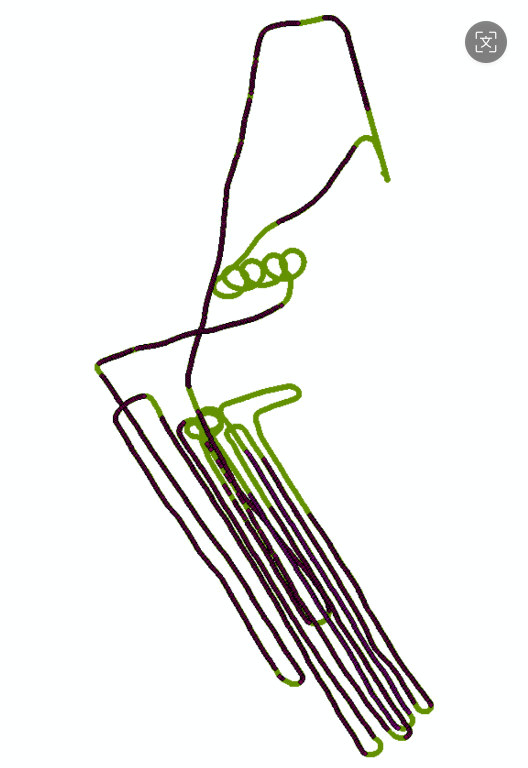
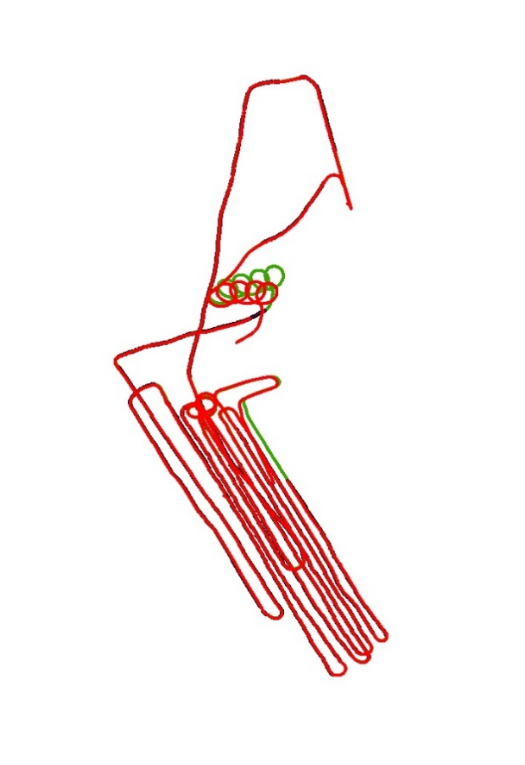
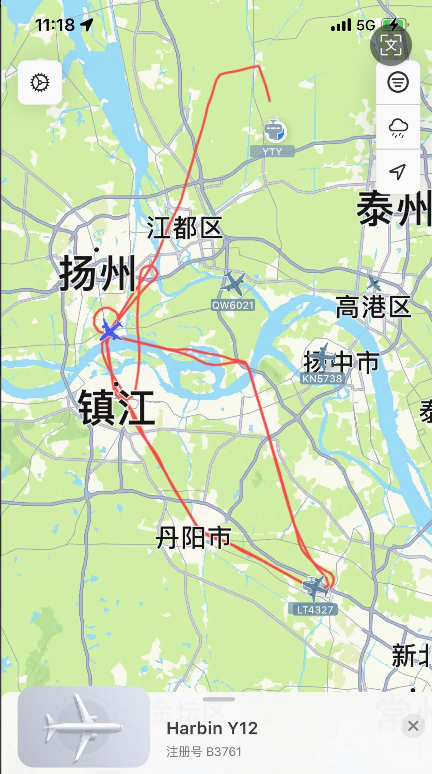
e. (December 2022 Yangzhou test results)On December 1-2, 2022, real-time combined navigation tests of the visual navigation system and inertial navigation system were conducted in Yangzhou, Jiangsu Province. A total of three flights were conducted, achieving long-term combined navigation using inertial navigation and visual navigation without satellite signals. The inertial navigation system needs to maintain high accuracy.


- Green dots indicate flight paths based on GPS,
- Purple dots indicate the positioning results of the visual navigation system,
- Red dots represent the results of the visual navigation system combined with inertial navigation (combined navigation results (speed accuracy 0.3 m/s, position accuracy 45 m))
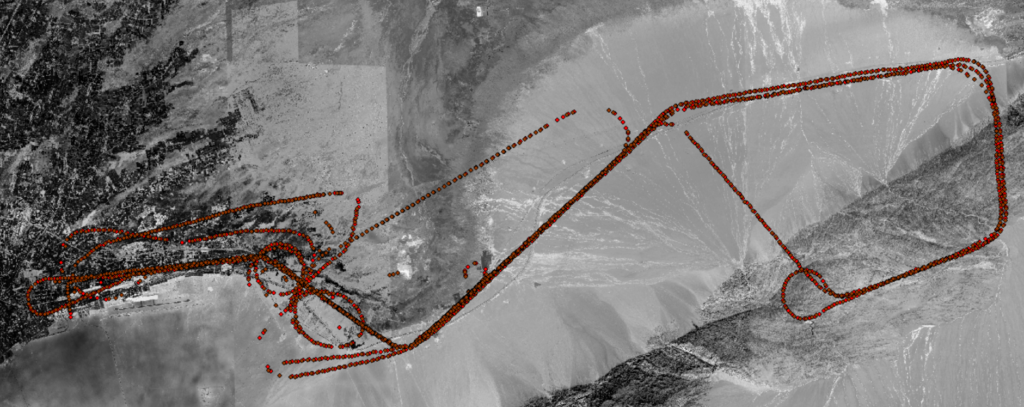
f. (July 2023 Dunhuang test results) In July 2023, tests were conducted on inertial/visual combined navigation and navigation parameters participating in flight control, with a total of five flights and 20 hours of flight time. The flight altitude ranged from 400 meters to 8,000 meters, and the flight area covered the suburbs, deserts, and mountainous terrain near Dunhuang.
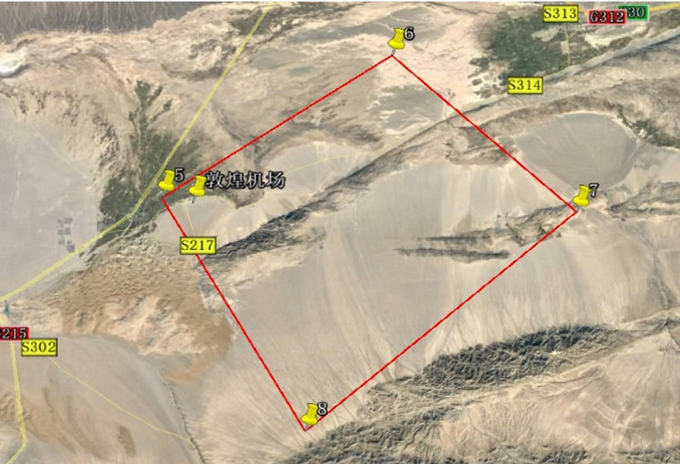

Visual navigation results on July 22: A total of 1,997 data points were obtained, with 1,527 output results and a positioning accuracy of 22 meters (1σ). Controlled flight lasted 1 hour and 5 minutes, the flight control is successful.

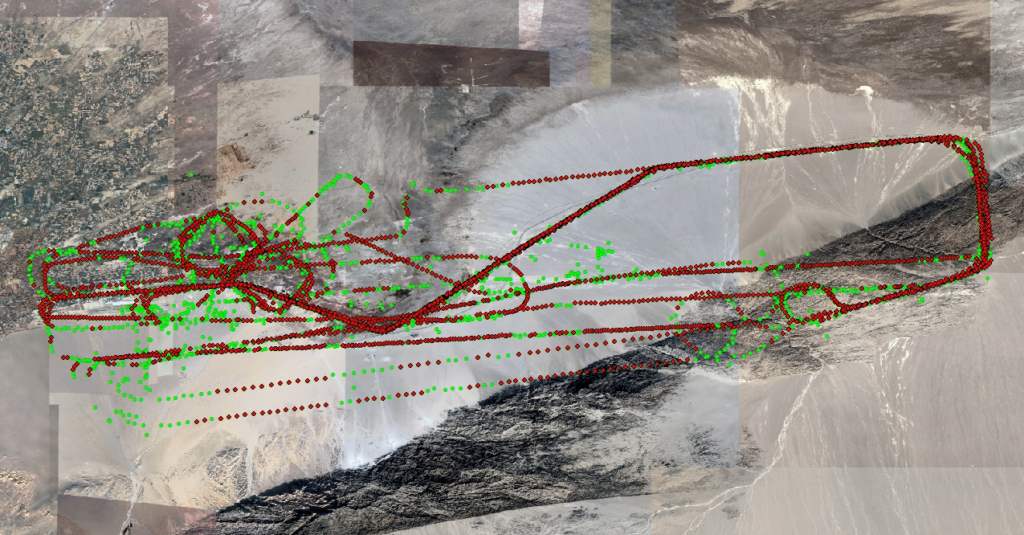
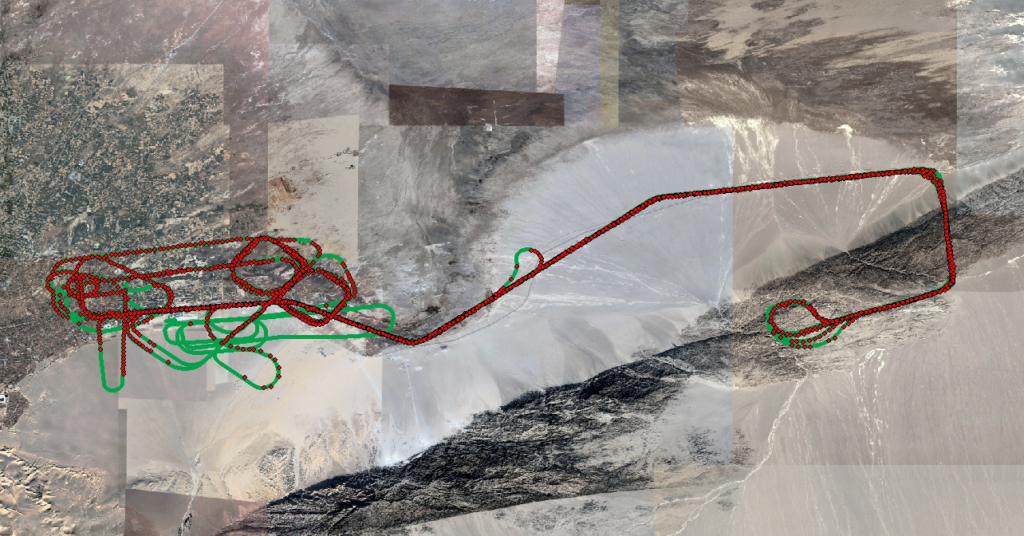
g. (October 2023 Dunhuang Test Results)In October 2023, tests were conducted on inertial/visual combined navigation and navigation parameters participating in flight control, with a total of two flights lasting nine hours. The flight altitude ranged from 400 meters to 8,000 meters, and the flight area covered the suburbs, deserts, Gobi Desert, and mountainous terrain near Dunhuang.

On the 17th, the test flight lasted a total of 5 hours and 35 minutes, during which the inertial/visual combined navigation parameters were used in real time for aircraft flight control for 1 hour and 40 minutes. A total of 4,997 valid data points were obtained, of which 3,194 were marked as usable, accounting for 64% of the total results. The statistical accuracy was 42.1 meters and 33.9 meters, and all results were correctly located.
| Ground Clearance | Latitude Direction Error | Longitude Direction Error | Number of results |
| Below 1000m | 9.74m | 9.08m | 176 |
| 1000~2500m | 11.54m | 10.73m | 110 |
| 2500~3500m | 30.56m | 28.51m | 571 |
| 3500~4500m | 33.07m | 32.77m | 775 |
| 4500~5500m | 35.88m | 37.72m | 555 |
| 5500~6500m | 45.85m | 38.76m | 193 |
| 6500m | 58.16m | 38.97m | 814 |
| statistical results | 42.1m | 33.9m | 3194 |
On the 18th, the test flight lasted a total of 3 hours and 58 minutes, during which the inertial/visual combined navigation parameters were used in real time for aircraft flight control for 1 hour and 31 minutes. A total of 3,738 valid data points were obtained, of which 2,753 were marked as usable, accounting for 73.6% of the total results. The statistical accuracy was 24.86 meters and 26.45 meters, and all results were correctly positioned.

| Ground clearance (m) | Latitude error (m) | Longitude error (m) | Number of results | Requirements (m) |
| Below 1000m | 11.66 | 11.05 | 240 | Height: 400+200m Error<50m |
| 1000~2500m | 13.38 | 10.79 | 149 | |
| 2500~3500m | 25.24 | 28.09 | 681 | |
| 3500~4500m | 25.82 | 29.18 | 103 | Height: 3000+500m Error<80m |
| 4500~5500m | 24.25 | 26.98 | 698 | |
| 5500~6500m | 22.61 | 26.00 | 78 | |
| 6500~6900m | 27.63 | 29.37 | 804 | Altitude 8000m Error<100m |
| Total | 24.86 | 26.45 | 2753 |
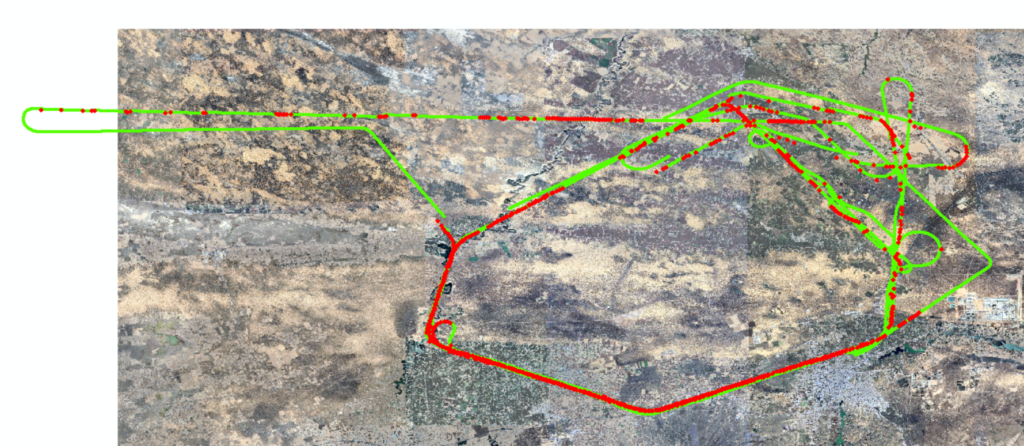
h. (April 2024 Jingbian test results) From April to May 2024, the visual navigation system participated in a drone flight test and completed five flights. The visual navigation system produced a total of 2,739 valid results, of which 988 were automatically judged to be usable. All usable results were correctly located, with no mislocations.
| Flight altitude | Number | Longitude error | Latitude error | Accuracy rate |
| Below 1000m | 264 | 13.93 | 13.16 | 100% |
| 1000~2000m | 46 | 12.82 | 26.32 | 100% |
| 2000~3000m | 357 | 29.42 | 33.91 | 100% |
| 3000~5000m | 115 | 45.74 | 47.67 | 100% |
| Higher than 5000m | 206 | 53.57 | 55.17 | 100% |
| Total | 988 | 35.02 | 37.37 | 100% |
i: (2025 tests) In 2025, multiple airborne tests were conducted in Huailai, Yanqing, Miyun, Zhuhai, and other locations to verify the performance of the visual navigation system under different flight platforms and different terrain and topographical conditions.

